Thats an exciting topic heading is'nt it ;-)
A traversal is just "visiting" each node in the tree in a specific order. I'll discuss Pre-order and Post-order traversals here. Performing an operation on each node and an important task for many applications. What is also important is the order in which the nodes are visited.
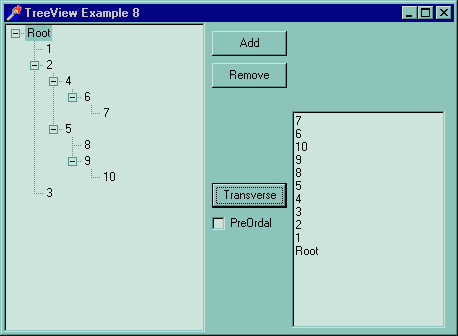
Here is example 8

| Control | Caption | Name |
| TButton | Add | but_Add |
| TButton | Remove | but_Remove |
| TTreeView | tv_eg1 | |
| TButton | Transverse | but_Transverse |
| TCheckBox | Pre-order | cbox_Pre-order |
| TMemo | mem_Order |
Clicking the traversal button with Pre-order checked will, obviously, start a Pre-order traversal. Without Pre-order checked a Post-order traversal is performed.
Here are the results of these two traversals with the tree structure show in the picture above.
| Traversals Order | Node order |
| Pre-order | Root -> 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 6 -> 7 -> 5 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> 3 |
| Post-order | 7 -> 6 -> 10 -> 9 -> 8 -> 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> Root |
The Pre-order traversal starts at the root, processes the root. Then moves one node left and processes that node. If there is not a left node it tries to move right. If there is no right node it moves up one and tries moves right. Look at the example and follow the path the traversal takes, its very simple once you see it.
A Post-order traversal is very similar in code to the Pre-order traversal. The difference is that the function first moves as far left as possible and then only processes the node. Again follow the path taken by the traversal in the example.
procedure EnumNodes( Node : TTreeNode;
Enum : EnumNodesProc;
pData : pointer;
bPre : boolean
);
begin
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Enter Function <------+ <---+
// | |
// Process this node (if Pre) | |
// | |
// If this node has children | |
// Call Enum with first child---+ |
// |
// If this node has siblings |
// Call Enum with next sibling---------+
//
//
// Process this node (if not Pre)
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// EnumNodesProc = procedure( Node : TTreeNode; pData : pointer );
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
if( Node = nil ) then
Exit;
{Preorder}
if( bPre ) then
Enum( Node, pData );
if( Node.GetFirstChild <> nil ) then
EnumNodes( Node.GetFirstChild, Enum, pData, bPre );
if( Node.GetNextSibling <> nil ) then
EnumNodes( Node.GetNextSibling, Enum, pData, bPre );
{Postorder}
if( not bPre ) then
Enum( Node, pData );
end;
As you can see the only differance between Pre-order and Post-order is when the node is proccessed. With recursive functions this makes a big differance.
This funtion uses a call back procedure that is defined
EnumNodesProc = procedure( Node : TTreeNode; pData : pointer );
The Node parameter is the node to be processed, the pData parameter is a user defined pointer.
All information on these www pages is copyright (©) 1997 Andre .v.d. Merwe And may not be copied or mirrored without my permission.